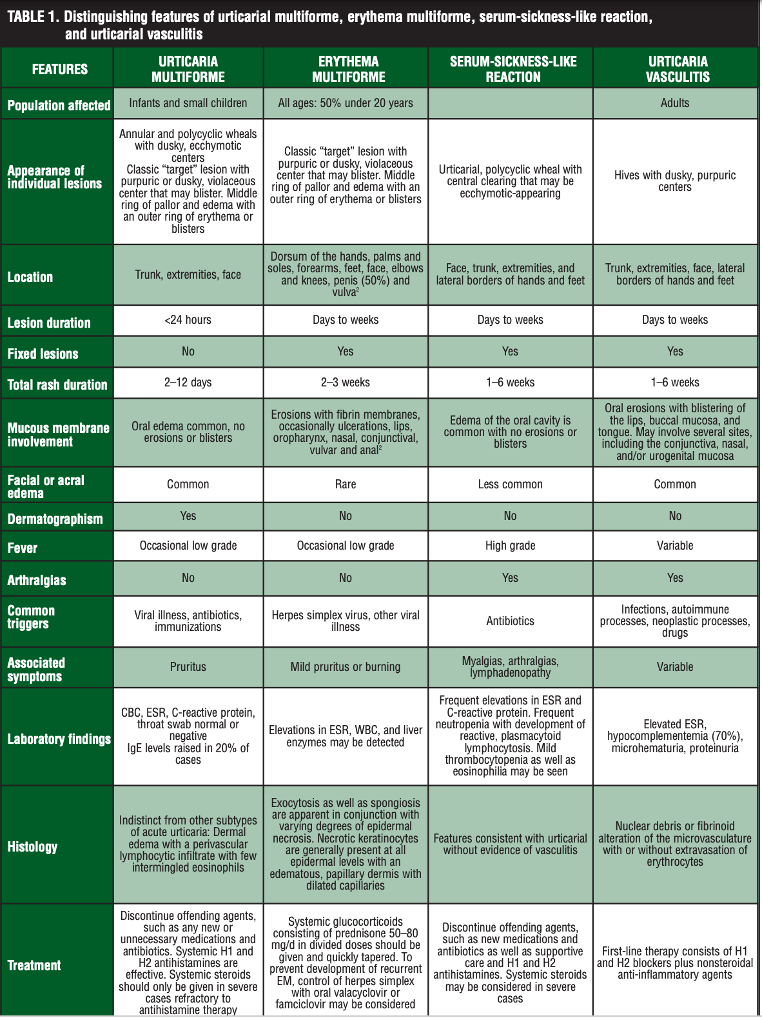
Differential Diagnosis Urticaria . The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissues, which produces. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a correct management and therapeutic approach.
from brownemblog.com
Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissues, which produces. It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a correct management and therapeutic approach. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases.
Recognizing the Differential Diagnoses for Erythema Multiforme — BROWN
Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a correct management and therapeutic approach. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissues, which produces. It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Acute urticaria Differential diagnosis and treatment Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.researchgate.net
Differential diagnosis of chronic urticaria Download Scientific Diagram Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.researchgate.net
Differential diagnosis of chronic urticaria Download Scientific Diagram Differential Diagnosis Urticaria It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From mungfali.com
Urticaria Classification Differential Diagnosis Urticaria The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissues, which produces. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. It is quite. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.jaad.org
Urticarial lesions If not urticaria, what else? The differential Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Differential Diagnosis of Urticarial Lesions Allergy Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From jamanetwork.com
Defining Urticarial Dermatitis JAMA Dermatology The JAMA Network Differential Diagnosis Urticaria It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a correct management and therapeutic approach. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.aafp.org
Acute and Chronic Urticaria Evaluation and Treatment AAFP Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Urticaria A Narrative Overview of Differential Diagnosis Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a correct management and therapeutic approach. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.jaad.org
Urticarial lesions If not urticaria, what else? The differential Differential Diagnosis Urticaria It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. Chronic. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.jaad.org
Urticarial lesions If not urticaria, what else? The differential Differential Diagnosis Urticaria It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. Anaphylaxis. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.researchgate.net
diagnosis algorithm for urticaria. Diagnostic algorithm for Differential Diagnosis Urticaria The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put in differential. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. Chronic. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Differential diagnosis between urticarial vasculitis and chronic Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a correct management and therapeutic approach. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. The difference between the two conditions is whether the. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.jaad.org
Urticarial lesions If not urticaria, what else? The differential Differential Diagnosis Urticaria From a clinical point of view, many skin conditions can mimic urticaria and their recognition is mandatory for a correct management and therapeutic approach. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. The difference between the two conditions is. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From mungfali.com
Urticaria Differential Diagnosis Differential Diagnosis Urticaria It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissues, which produces. Urticaria,. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.mdpi.com
Biomedicines Free FullText Urticaria A Narrative Overview of Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissues, which produces. The diagnosis of urticaria is usually straightforward, but several mimickers need to. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 2 from Urticarial lesions if not urticaria, what else? The Differential Diagnosis Urticaria It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. Chronic urticaria is idiopathic in 80% to 90% of cases. Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. In this section we present a heterogeneous group of cutaneous inflammatory conditions that can be put. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Differential Diagnosis of Urticarial Lesions Allergy Differential Diagnosis Urticaria Urticaria, also known as welts, hives, or wheals, is characterized by the appearance of intensely pruritic erythematous. Anaphylaxis must be ruled out. It is quite easy to diagnose based on clinical appearance and anamnesis. The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and. Differential Diagnosis Urticaria.